Penetration testing, often referred to as ‘pen testing,’ is a crucial method for identifying and addressing an organization’s weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and security flaws. Used by more than 75% of companies worldwide, pen testing helps organizations stay one step ahead of hackers and malicious actors, by allowing them to identify the weaknesses in their system, before others do.
As a proactive approach to fortifying a company’s security strategy, effective penetration tests can help companies adhere to compliance standards, secure sensitive information, avoid data breaches, save money, and defend their reputations with customers.
As experts in vulnerability management services, we’ve created this guide to introduce you to the benefits of internal and external penetration testing and help you decide which strategy is right for your company’s needs.
What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing, sometimes referred to as ethical hacking or pen testing, is the practice of simulating a cyberattack against an organization to evaluate the systems, networks, and applications of that business for signs of weaknesses or vulnerabilities.
Penetration tests can be internal or external, depending on the goals of the company. However, in most penetration tests, there are multiple stages involved. Usually, there’s an initial planning stage, where the scope, objectives, and rules of the test are defined. Next, there’s a scanning stage, where intuitive tools and techniques are deployed to identify potential vulnerabilities and gather information about the target system.
In the gaining access phase, internal or external pen testers exploit the discovered vulnerabilities in the system to attempt to gain unauthorized access. If they gain access, they attempt to maintain it for as long as possible, often trying to escalate their privileges or extract additional data or value from the environment.
Following this process, an analysis phase is conducted to compile the findings of the test, assess the impact, and explore recommendations for remediation.
This process might sound complex and unusual, but it allows businesses to proactively identify and address security weaknesses before malicious attackers do. Penetration testing can be a phenomenal way to strengthen a company’s defenses, protect sensitive data, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Defining Internal Penetration Testing
When companies invest in internal penetration testing, they attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in their internal network from an insider’s perspective. It involves simulating an insider threat, where an attacker has bypassed external cybersecurity measures and is attempting to exploit vulnerabilities within the internal network.
Internal penetration tests are often essential for evaluating the security of your internal systems, networks, and applications. It can involve examining everything from computer systems and access points to local servers for evidence of a vulnerability.
Usually, the process begins with assessing the network’s architecture, such as firewalls, switches, and routers, before probing applications and systems. Testers employ a range of techniques to exploit vulnerabilities and will attempt to escalate their privileges once they’re inside the system.
An internal penetration test can help determine the impact of internal security controls and uncover potential insider threats. Plus, after a network breach, it can help ensure no further vulnerabilities remain in the system that could be exploited in the future. It’s also a great way to examine employee access controls and make sure the business is adhering to compliance guidelines.
Defining External Penetration Testing
Unlike internal pen testing processes, external penetration testing involves simulating an external attack on the perimeter defenses of an organization. An individual mimics the actions of a potential outside threat to determine how well the company’s security systems can withstand potential threats.
Similar to internal pen tests, external penetration tests often begin with reconnaissance and risk assessments, where testers gather information about the external infrastructure of the target. These ethical hackers then scan for open ports, potential vulnerabilities, and issues with websites, web applications, and network services.
Ultimately, the focus of external penetration testing is on identifying vulnerabilities in external defenses, assessing the potential value of perimeter security measures, and uncovering opportunities to protect against unauthorized access to a system.
This type of testing is important in many scenarios. Developers run these tests before launching a new web application to ensure it’s secure. Businesses run external tests after making changes to network infrastructure, to ensure new vulnerabilities haven’t emerged. They also use external tests to ensure continued compliance with regulatory requirements.
Internal vs External Penetration Testing: The Differences
Although both internal and external penetration tests offer valuable ways to assess the vulnerabilities of a system, there are some core differences between them. First, the focus of both strategies is very different. Internal penetration testing concentrates on the internal network, simulating threats that originate within an organization.
This includes evaluating internal systems, networks, and applications to uncover vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious insiders or attackers who have breached external defenses. External penetration testing, on the other hand, focuses on the perimeter defenses of the organization. It looks at the vulnerabilities in assets like network services, web applications, and websites.
The goal is to simulate an attack that originates outside of an organization, to identify potential weaknesses and entry points that might be used by hackers. Other key differences include:
- Methodologies and tools used: Internal penetration testing often requires detailed knowledge of internal systems. Testers use techniques like network sniffing and privilege escalation to explore vulnerabilities. External testing concentrates on finding entry points from outside of the network with vulnerability and port scanning, as well as social engineering.
- The goals: As mentioned above, the goal of internal penetration testing is to uncover internal vulnerabilities and insider threats and assess the impact of internal security controls. The goal of external penetration testing involves finding weaknesses that could be taken advantage of from outside of the organization, to minimize the risk of breaches.
- Scope and impact: Internal penetration testing can uncover deeper, complex issues within the organization, highlighting potential security gaps and how internal systems interact. External penetration testing primarily focuses on preventing breaches from occurring in the first place, ensuring the right security precautions are in place.
Benefits of Internal Penetration Testing
Conducting an internal penetration test is a beneficial way to explore the internal aspects of an organization’s security and minimize threats. The strategy helps companies to:
- Uncover internal vulnerabilities: An internal pen test helps detect potential threats within the organization, including malicious or negligent employee behavior. It can also spot vulnerabilities that might be overlooked by external assessments, such as misconfigured devices or outdated software that may lead to risks.
- Ensure security measures are effective: Internal penetration testing helps to ensure existing security measures, like firewalls, access controls, and intrusion detection systems are effectively mitigating risks. It can also help validate a company’s ability to detect and respond rapidly to internal threats when they emerge.
- Strengthen network defenses: Internal testing pinpoints weaknesses within the network or internal systems, such as poorly secured systems and sensitive areas. This allows organizations to take corrective actions to strengthen their security and reduce their exposure to unnecessary risks.
Benefits of External Penetration Testing
External penetration testing also delivers a host of benefits to businesses, helping them to optimize their security posture by:
- Identifying vulnerabilities: External penetration tests reveal potential vulnerabilities in accessible systems like web applications, websites, and network services. These vulnerabilities might include unpatched software or exposed parts. By identifying these issues in advance, companies can implement new protection measures.
- Improving perimeter defenses: By testing the performance of intrusion detection systems and security configurations and simulating real-world attacks from external actors, companies can improve their perimeter defenses. They can discover new ways to ensure their systems can withstand external attacks.
- Strengthening network defenses: External testing helps companies identify and remediate weaknesses in systems and applications that external actors can access. This reduces the risk of successful external attacks, improves compliance with industry standards, and leads to a significant reduction in potential threats.
Choosing the Right Penetration Testing Approach for Your Business
Ultimately, both an internal and external penetration test can be extremely beneficial to businesses. Which type of system or network penetration testing strategy you prioritize will depend on a few factors, such as your current security posture, the compliance requirements you need to adhere to, and the security concerns you’ve discovered for your organization.
A comprehensive security strategy, which involves leveraging MDR services to run both internal and external penetration testing is usually the best option for most companies. It ensures you can take a holistic approach to identify and eliminate various types of vulnerability.
Zyston’s managed cybersecurity solutions offer businesses of all sizes and industries a comprehensive strategy for implementing penetration testing. We can run both internal and external network penetration testing and vulnerability scanning strategies, to identify every potential weakness in your system.
Contact Zyston today to arrange an initial vulnerability assessment. Our team will analyze your system and network and provide advice on which critical assets to prioritize, and how to schedule regular penetration tests that improve your security standing.
Protecting your Business with Penetration Testing
External and internal penetration testing strategies play vital roles in improving your company’s cybersecurity efforts. Combining internal and external penetration testing will help you identify vulnerabilities both within your organization and in your external perimeter.
With this approach, businesses can pinpoint all of the potential risks that could harm their compliance standards and lead to expensive or complex security breaches.
Take a proactive approach to securing your network, by integrating the benefits of regular penetration testing for both internal and external systems into your cybersecurity strategy today.
Contact Zyston, the leader in managed security services for businesses, to arrange a consultation with our team and discover the benefits of our expert penetration testing strategies firsthand. We’ll help to ensure your networks are secured against both internal and external threats, giving you the peace of mind you need to grow your business safely.
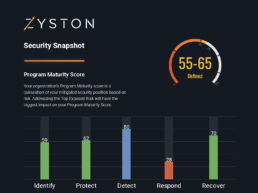
CyberCast Security Reporting
Security reporting that speaks business
Zyston CyberCAST brings the world of cybersecurity metrics up out of the weeds and into the hands of executive decision makers so nothing gets lost in translation. With CyberCAST, your organization gets clear visibility on security risks and also how your organization scores against your industry peers.





















