In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses face an increasing number of sophisticated cyber threats. According to the National Cyber Security Alliance, 60% of small businesses go out of business within six months of a cyber attack.
Protecting your organization from these threats requires a proactive and thorough approach. A comprehensive cyber security risk assessment report is a crucial tool in this endeavor. It provides an in-depth analysis of your organization’s IT environment, identifying vulnerabilities and potential risks, and offers actionable insights to safeguard sensitive information and ensure resilience against cyber attacks. This report not only helps in pinpointing areas of weakness but also equips you with the strategies needed to fortify your defenses and maintain a robust security posture in the face of evolving cyber threats.
In this article, we’ll explore what a cyber security risk assessment report entails, the benefits of conducting one, and the step-by-step process involved. By the end, you’ll understand how to enhance your organization’s security posture and make informed decisions to mitigate potential threats.
What Is a Cyber Security Risk Assessment Report?
A cyber security risk assessment report is a detailed evaluation of your organization’s IT environment, analyzing potential security risks and vulnerabilities. Here’s what it typically includes:
Key Components of a Cyber Security Risk Assessment
Asset Identification and Valuation
The first step in a cyber security risk assessment is to identify and value the organization’s critical assets. This involves cataloging all hardware, software, data, and network resources. Each asset is then assigned a value based on its importance to the organization’s operations, the sensitivity of the information it holds, and the potential impact of its compromise. This valuation helps prioritize which assets need the most robust protection.
Threat and Vulnerability Analysis
After identifying critical assets, the next step is to assess potential threats and identify vulnerabilities. This involves understanding the various threats that could target the organization, such as cybercriminals, insider threats, natural disasters, or system failures. Concurrently, a vulnerability assessment is conducted to detect weaknesses within the organization’s systems and networks that could be exploited by these threats. This dual analysis helps create a comprehensive picture of the risk landscape.
Risk Evaluation and Scoring
With the identified threats and vulnerabilities, the next phase involves evaluating and scoring the risks. This is done by determining the likelihood of each threat exploiting a vulnerability and the potential impact if it occurs. Risk scores are then assigned to each identified risk, often using a standardized scoring system like the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). These scores help prioritize risks, focusing attention and resources on the most critical areas.
Recommended Mitigation Strategies
Based on the risk scores, actionable mitigation strategies are developed. These strategies aim to reduce the likelihood of risks materializing and minimize their impact if they do. Recommendations can include technical controls (such as installing firewalls and encryption), process improvements (like regular security audits), and policy changes (such as updating access control policies). These tailored strategies provide a clear path forward to strengthen the organization’s security posture.
Objectives and Outcomes
Improving Security Posture
A primary objective of the cyber security risk assessment is to enhance the organization’s overall security posture. The assessment provides a detailed roadmap of security measures that need to be implemented, helping to build robust defenses against potential threats. By systematically addressing identified risks, the organization can significantly reduce its vulnerability to cyber-attacks.
Informed Decision-Making
The insights gained from the risk assessment enable stakeholders to make informed, data-driven decisions regarding security investments and policies. By understanding where the most significant risks lie and what their potential impacts are, leaders can allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that security efforts are both efficient and effective.
Compliance
Adhering to legal and regulatory requirements is a crucial outcome of conducting a cyber security risk assessment. Many industries are subject to strict regulations regarding data protection and cyber security. A comprehensive risk assessment helps ensure that the organization meets these requirements, avoiding potential legal repercussions and building trust with customers and partners.
At Zyston, our team of cybersecurity experts has extensive experience in conducting thorough risk assessments and developing robust security strategies for businesses of all sizes. Our proven methodologies and industry-leading tools ensure that we provide actionable insights and effective solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Preparation for the Assessment
Define the Scope:
- Assessment Boundaries: Determine the systems, networks, and applications to be evaluated.
- Critical Assets: Identify the most valuable data and systems that need protection.
Importance of Identifying Assets and Stakeholders:
- Key Information Systems: Recognize essential data repositories and information systems.
- Engage Stakeholders: Understand their concerns and requirements to tailor the assessment effectively.
Gathering Documentation:
- Network Diagrams and System Inventories: Collect detailed documentation of your IT environment.
- Security Policies and Compliance Requirements: Review existing security measures and regulatory obligations.
Conducting the Assessment
Methodologies:
- Qualitative Analysis: Subjective evaluation based on expert judgment.
- Quantitative Analysis: Objective evaluation using numerical data and metrics.
Identifying Threats and Vulnerabilities:
- Threat Modeling: Identify potential adversaries and their attack vectors.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Detect weaknesses in systems and applications.
Assessing Risks:
- Likelihood: Estimate the probability of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
- Impact: Determine the potential damage to the organization if the risk materializes.
Analyzing the Data
Techniques:
- Risk Matrices: Visualize and prioritize risks.
- Statistical Models: Quantify risk levels using data-driven approaches.
Prioritizing Risks:
- Severity and Impact: Rank risks based on their potential impact and likelihood.
- High-Priority Risks: Focus on those requiring immediate attention.
Determining Risk Levels:
- Standardized Scoring Systems: Use systems like CVSS for evaluating vulnerabilities.
- Technical and Business Impact: Consider both perspectives in risk assessment.
Reporting the Findings
Structure of the Report:
- Executive Summary: High-level overview for stakeholders.
- Detailed Findings: In-depth analysis for technical teams.
- Actionable Recommendations: Specific steps for mitigation.
Presenting Findings:
- Visual Aids: Use charts and graphs to illustrate key points.
- SMART Recommendations: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound advice.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Technical Controls: Implement firewalls, encryption, and other technical measures.
- Process Improvements: Conduct regular security audits and enhance procedures.
- Policy Changes: Update access controls and other security policies.
Implementing Recommendations
Developing a Mitigation Plan:
- Action Steps: Outline steps to address each identified risk.
- Responsibilities and Timelines: Assign tasks and set deadlines for implementation.
Implementing Security Controls:
- Technical Controls: Deploy new tools and update software.
- Administrative Controls: Train employees and update policies.
Roles and Responsibilities:
- Security Team: Lead the implementation efforts.
- IT Staff: Support technical deployment.
- Management: Provide oversight and resources.
Continuous Monitoring and Review
Ongoing Monitoring:
- Proactive Security Posture: Maintain vigilance against new threats.
- Timely Detection and Response: Quickly address emerging risks.
Regular Updates:
- Periodic Reassessments: Conduct regular reviews of the risk assessment report.
- Incorporate Changes: Adapt to new IT environments and threat landscapes.
Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback Loops: Learn from past incidents and adjust security measures.
- New Insights and Trends: Stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Conclusion
Conducting a cyber security risk assessment report is crucial for identifying and mitigating risks systematically. A well-documented report not only enhances your security resilience but also ensures compliance with best practices and regulatory requirements.
Zyston’s fully managed cybersecurity solutions offer expertise in risk assessments, continuous threat exposure management, and response services, supporting businesses in maintaining a robust security posture. Protect your organization today with our comprehensive cybersecurity services.
Explore our Cybersecurity Risk Assessment Services and take the first step toward securing your business. Learn more about our CyberCAST Security Snapshot Assessment and our Managed Cybersecurity Services for ongoing protection and peace of mind.
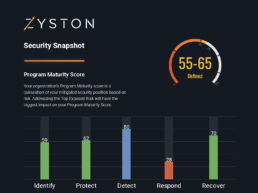
CyberCast Security Reporting
Security reporting that speaks business
Zyston CyberCAST brings the world of cybersecurity metrics up out of the weeds and into the hands of executive decision makers so nothing gets lost in translation. With CyberCAST, your organization gets clear visibility on security risks and also how your organization scores against your industry peers.



















